Introduction
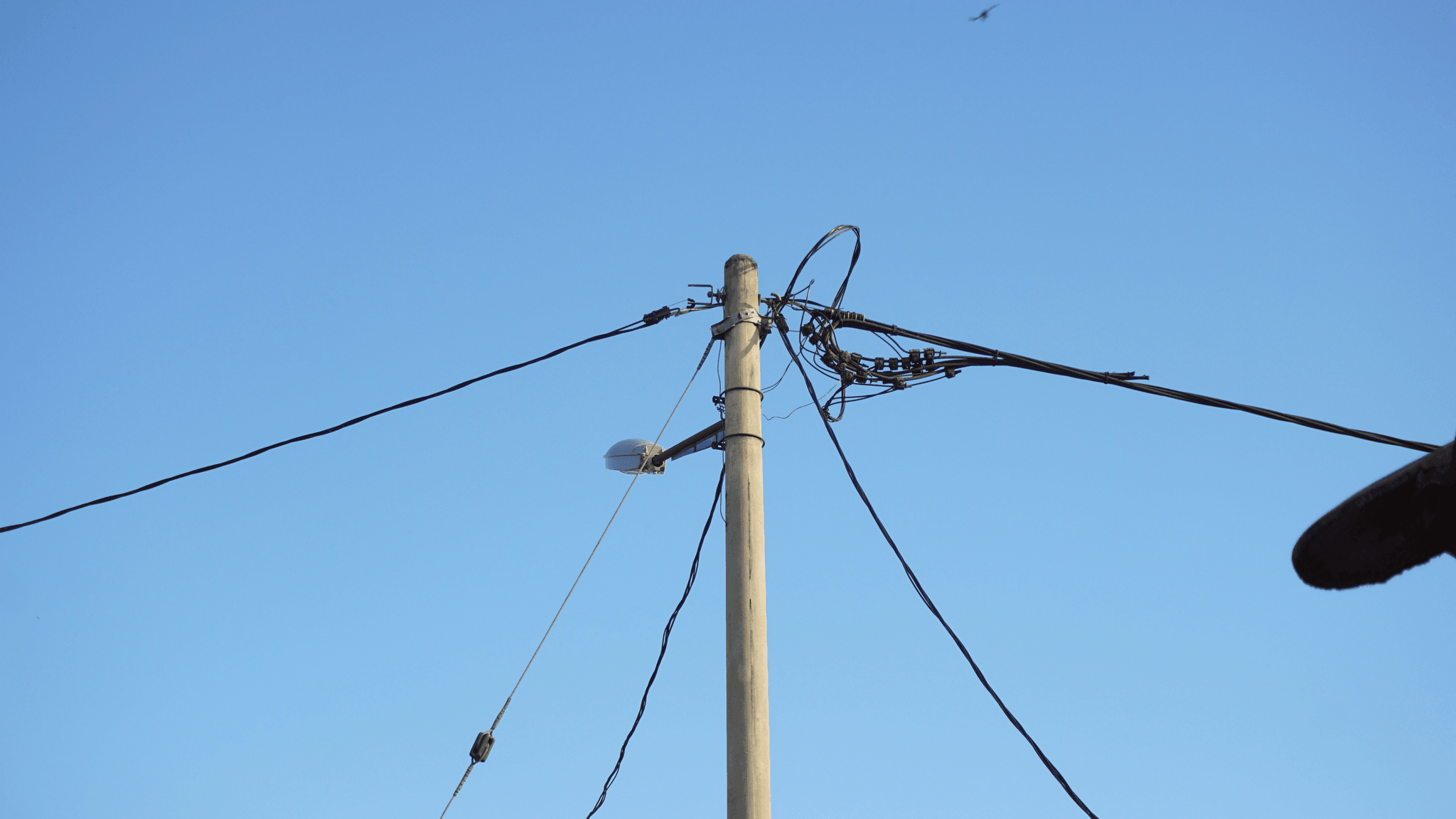

In the fast-paced world of modern infrastructure, communication and power transmission are more intertwined than ever. Enter OPGW, or Optical Ground Wire, a game-changing technology that combines these essential functions into one robust solution. With its unique design and capabilities, OPGW cable is becoming a staple in electrical grids worldwide.
Overview of OPGW Cable
OPGW cable is a specialized type of fiber optic cable that serves dual purposes: it acts as both a ground wire for electrical transmission lines and a conduit for high-speed data communication. The composition of OPGW typically includes steel and aluminum strands encasing optical fibers, which ensures durability while providing the necessary strength to withstand environmental challenges. This innovative design makes OPGW an attractive option for utilities looking to upgrade their infrastructure without compromising safety or performance.
Importance of OPGW in Modern Infrastructure
The significance of OPGW in today's infrastructure cannot be overstated; it plays a crucial role in enhancing the reliability and efficiency of electrical grids. As we increasingly rely on digital communication for monitoring systems, integrating this technology into power transmission lines becomes vital. Moreover, with the rise of renewable energy sources, the need for effective communication between grid components has never been more critical—this is where OPGW truly shines.
Key Advantages of Using OPGW
One key advantage of using OPGW is its ability to facilitate real-time monitoring and control over electrical systems, which can help prevent outages and improve overall grid stability. Additionally, when considering what is the difference between OPGW and Earth Wire?, it's clear that while both serve protective roles, only OPGW offers high-capacity fiber optics for data transmission alongside grounding functionality. Furthermore, understanding what is OPGW splicing reveals how seamless connections can be made to maintain signal integrity—making it an indispensable tool in modern telecommunications.
What is OPGW Cable?

OPGW, or Optical Ground Wire, is a specialized cable that combines the functions of grounding and communication. It typically consists of optical fibers encased within a metallic sheath, which provides both mechanical strength and electrical conductivity. This unique composition allows OPGW to serve dual purposes: protecting overhead power lines from lightning strikes while also facilitating high-speed data transmission.
Definition and Composition
At its core, OPGW cable is designed to be installed on overhead transmission lines, where it acts as both a ground wire and an optical fiber communication medium. The composition includes various layers: an outer aluminum or steel layer for strength, followed by insulation materials that protect the internal optical fibers. These fibers are crucial for transmitting data signals over long distances without significant loss in quality.
How OPGW Works
The functionality of OPGW hinges on its dual capabilities—grounding and communication. When installed on transmission lines, it effectively dissipates electrical surges caused by lightning strikes while simultaneously allowing for real-time communication between grid operators through the embedded optical fibers. This integration enhances the reliability of electrical grids and enables advanced monitoring systems to ensure optimal performance.
Typical Applications of OPGW
OPGW finds its way into various applications across multiple sectors due to its versatile nature. In electrical utilities, it's primarily used in transmission lines where it supports both power delivery and data communication essential for grid management. Additionally, industries such as telecommunications leverage OPGW cables for their robust performance in harsh environments while providing high-speed internet connectivity.
OPGW in Transmission Line

The integration of OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) into transmission lines has revolutionized the way electrical grids operate. By combining the functions of a ground wire and a communication medium, OPGW enhances both safety and efficiency in power transmission. Understanding its role is crucial for appreciating modern infrastructure's capabilities.
Role of OPGW in Electrical Grids
OPGW plays a pivotal role in electrical grids by providing essential grounding while simultaneously facilitating high-speed data transmission. This dual functionality not only protects the infrastructure from lightning strikes but also enables utilities to monitor grid performance in real-time. The result is a more resilient system that can adapt to changing demands and prevent outages.
Moreover, the use of OPGW cable helps utilities comply with regulatory requirements for communication systems within their networks. By integrating communication capabilities directly into the transmission line structure, operators can streamline maintenance processes and reduce costs associated with separate communication installations. Ultimately, this leads to improved reliability and operational efficiency across the grid.
Enhancing Communication and Monitoring
One of the standout features of OPGW is its ability to enhance communication and monitoring within electrical grids significantly. With integrated fiber optic technology, OPGW allows for continuous data collection on various parameters such as voltage levels, temperature fluctuations, and potential faults along transmission lines. This real-time monitoring capability empowers utilities to make informed decisions quickly.
In addition to improving operational oversight, the enhanced communication facilitated by OPGW also supports advanced automation systems that optimize power distribution based on demand fluctuations. This means that energy providers can react swiftly to any disruptions or inefficiencies—ultimately leading to reduced downtime and improved service reliability for consumers. As we explore further into What is the difference between OPGW and ADSS fiber optic cable?, it becomes evident that while both serve critical roles, their applications differ based on specific needs within an electrical grid context.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
Real-world applications of OPGW illustrate its significant impact on modernizing electrical infrastructure globally. For instance, a major utility company implemented an extensive network of OPGW across its transmission lines, resulting in enhanced fault detection capabilities that reduced outage response times by nearly 30%. Such success stories highlight how effective integration of this technology can lead to tangible benefits for both providers and consumers alike.
Another notable case involved upgrading existing lines with new OPGW installations alongside traditional earth wires—a move prompted by inquiries like What is the difference between OPGW and Earth Wire? The transition not only improved safety through better grounding but also allowed for seamless communications without necessitating additional construction efforts or expenses typically associated with separate systems.
As we delve deeper into comparisons like What is the difference between OPGW and OPPC?, it's clear that understanding these distinctions can guide stakeholders in making informed choices about their infrastructure investments moving forward.
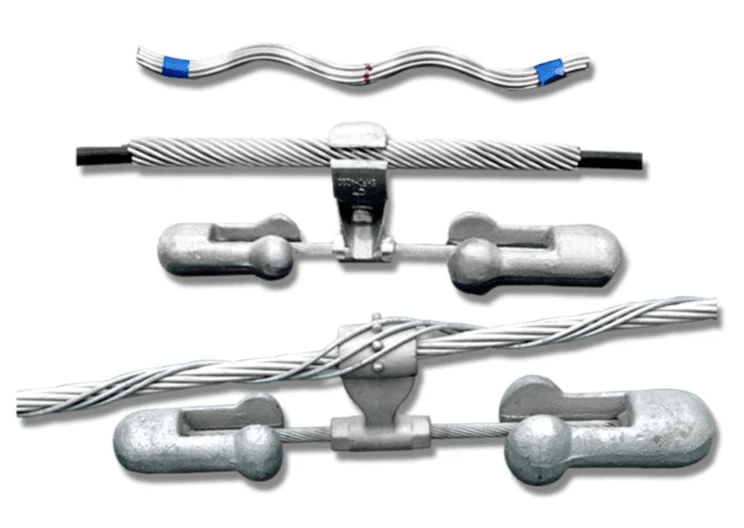
What is OPGW Splicing?

OPGW splicing is a critical process in the installation and maintenance of Optical Ground Wire (OPGW) cables, which serve dual purposes in electrical transmission lines. This section delves into the intricacies of OPGW splicing, highlighting its significance, tools used, and best practices to ensure optimal performance. Understanding what OPGW splicing entails is essential for anyone involved in modern infrastructure projects.
The Splicing Process Explained
The splicing process for OPGW involves joining two fiber optic ends to create a continuous optical pathway, ensuring seamless data transmission across electrical grids. Typically, this process requires precise alignment of the fibers within a splice tray, followed by fusion or mechanical splicing techniques that permanently bond the fibers together. Properly executed OPGW splicing minimizes signal loss and enhances the reliability of communication systems integrated within transmission lines.
Tools and Techniques for OPGW Splicing
To successfully splice OPGW cables, technicians rely on specialized tools such as fusion splicers, optical time-domain reflectometers (OTDR), and cleavers. Fusion splicers heat the ends of the fibers until they meld together seamlessly while OTDRs help identify faults or losses in the cable after installation. Additionally, understanding various techniques like ribbon splicing or mass fusion can enhance efficiency and accuracy when dealing with multiple fibers in one go.
Importance of Proper Splicing in Performance
Proper OPGW splicing plays a pivotal role in maintaining high-performance standards for both data transmission and electrical safety within transmission lines. Inadequate or poorly executed splices can lead to significant signal degradation or even complete system failures—an outcome no one wants when relying on advanced communication networks. Therefore, investing time and resources into skilled technicians who understand what is OPGW splicing can pay off immensely by ensuring robust performance for years to come.
What is the Difference Between OPGW and Earth Wire?

Functional Differences Explained
OPGW is a dual-purpose cable that combines the functions of grounding and communication within a single structure. It not only protects against lightning strikes but also allows for data transmission through integrated optical fibers. In contrast, earth wire primarily serves as a grounding mechanism to safeguard electrical equipment from surges without any communication capabilities.
The versatility of OPGW makes it particularly valuable in scenarios where both grounding and data transfer are necessary, such as in smart grids and advanced monitoring systems. With OPGW in transmission lines, utilities can streamline operations while enhancing safety measures. On the other hand, earth wires remain essential components for basic grounding needs but lack the advanced features offered by OPGW cables.
Safety and Performance Comparisons
When comparing safety features, OPGW provides an additional layer of protection through its fiber optics that can monitor line conditions in real-time. This capability allows for proactive maintenance strategies that can prevent catastrophic failures or outages before they occur. In contrast, while earth wires are effective at dissipating electrical surges to ground, they do not provide any monitoring capabilities.
Performance-wise, OPGW generally offers superior resilience against environmental factors due to its composite design that can withstand harsh weather conditions better than traditional earth wires. Moreover, since OPGW integrates communication technology directly into the cable system, it enhances overall grid efficiency by allowing for immediate data relay regarding line status or faults. Earth wire may suffice for basic protection but falls short when it comes to modern demands for data integration and smart technology applications.
Choosing Between OPGW and Earth Wire
Choosing between OPGW and earth wire largely depends on specific project requirements and future needs of infrastructure development. If a project aims to incorporate advanced monitoring systems alongside reliable grounding solutions—such as what is often seen with smart grids—then investing in OPGW would be advantageous due to its multifunctional nature. However, if you’re working on a more straightforward application where basic grounding suffices without any need for communication capabilities, then an earth wire could be your best bet.
In summary, understanding What is the difference between OPGW and Earth Wire? boils down to recognizing how each serves distinct purposes within electrical frameworks today—especially with growing demands for efficiency and safety in energy distribution networks. As we move toward more interconnected systems using technologies like What is OPGW splicing? or What is the difference between OPGW and OPPC?, making informed choices becomes increasingly vital.
What is the Difference Between OPGW and OPPC?

When discussing advancements in fiber optic technology, two acronyms often come up: OPGW and OPPC. While both serve critical roles in enhancing communication and power transmission, their structural differences significantly influence their applications and efficiency. Understanding what distinguishes these two types of cables can help engineers and project managers make informed choices for their infrastructure needs.
Structural Differences and Uses
OPGW, or Optical Ground Wire, is a cable that combines optical fibers with a metallic wire designed to protect against lightning strikes while providing communication capabilities. Its structure typically consists of multiple optical fibers encased within a protective metal sheath, which also serves as a grounding mechanism for electrical systems. In contrast, OPPC, or Optical Phase Conductor, primarily functions as a power conductor with integrated optical fibers but lacks the same level of protection against environmental factors that OPGW offers.
The primary use of OPGW is in overhead power lines where it can provide dual functionality—grounding for electrical safety while facilitating high-speed data transmission. On the other hand, OPPC is often utilized in scenarios where space is limited or where existing power lines can be upgraded to include fiber optics without additional infrastructure changes. This means that while both serve essential roles in modern telecommunications and electrical grids, their structural designs dictate different applications.
Applications in Different Environments
In environments prone to severe weather conditions or where lightning strikes are common, OPGW proves invaluable due to its protective qualities. It’s commonly used on high-voltage transmission lines not only for communication purposes but also to safeguard vital equipment from electrical surges caused by storms or other natural events. Additionally, OPGW’s ability to withstand harsh conditions makes it suitable for remote areas that require reliable data transfer alongside electricity supply.
Conversely, OPPC shines in urban settings where space constraints necessitate innovative solutions for integrating fiber optics into existing infrastructure without extensive modifications. It allows utilities to enhance their communication capabilities without disrupting the physical landscape significantly—ideal for cities bustling with activity and densely packed buildings. Thus, each cable type serves distinct needs based on environmental considerations and existing infrastructure challenges.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
When evaluating cost-effectiveness between OPGW and OPPC cables, several factors come into play including installation costs, maintenance expenses, and overall operational efficiency over time. While OPGW may have higher initial installation costs due to its robust design requirements meant for protection against environmental hazards, its longevity often translates into lower maintenance costs down the line—making it an attractive option for long-term projects.
On the flip side, OPPC tends to be more budget-friendly upfront because it utilizes existing power line structures without requiring substantial alterations or new installations from scratch. However, this might lead to higher maintenance costs if the environment poses risks like corrosion or damage from weather elements since it lacks some protective features found in OPGW designs. Ultimately, choosing between these two options hinges on balancing short-term budgetary constraints with long-term performance expectations.
What is the Difference Between OPGW and ADSS Fiber Optic Cable?

When it comes to fiber optic cables, two prominent players in the game are OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) and ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting) cables. While both serve critical roles in modern telecommunications, they differ significantly in design, functionality, and application. Understanding these differences can help you determine which cable best meets your specific needs.
Comparing Design and Functionality
OPGW is designed primarily for use on overhead power lines, combining the functions of grounding and communication by integrating optical fibers within a metallic structure. Its dual purpose not only protects electrical infrastructure but also provides high-speed data transmission capabilities. On the other hand, ADSS cables are constructed entirely of non-metallic materials, allowing them to be installed in a variety of environments without being influenced by electrical interference or needing additional support structures.
The difference between OPGW and ADSS fiber optic cable becomes apparent when considering their installation methods as well. OPGW requires existing power line infrastructure for support, making it ideal for utility companies looking to enhance their communication systems without significant additional investment. Conversely, ADSS can be strung between poles independently without relying on any existing structures, making it versatile for urban areas where space is limited.
Advantages of Each Type
One of the key advantages of OPGW is its ability to provide both grounding protection and high-speed communication simultaneously; this makes it a cost-effective choice for utility companies operating large networks. Furthermore, because OPGW is integrated into existing transmission lines, it minimizes installation costs while maximizing efficiency in data transfer across vast distances. In contrast, ADSS offers flexibility in installation locations since it does not require metallic supports; this makes it particularly useful in rural or remote areas.
Another benefit of OPGW lies in its robust construction that withstands harsh environmental conditions while providing reliable performance over time—an essential factor when considering the longevity of network infrastructure. Meanwhile, ADSS excels at avoiding electromagnetic interference due to its all-dielectric design; this characteristic enhances signal integrity for sensitive applications such as video surveillance or advanced telemetry systems.
Best Use Cases for OPGW vs. ADSS
When evaluating best use cases between OPGW and ADSS fiber optic cables, it's crucial to consider your specific requirements—whether they lean toward enhanced electrical grid performance or independent telecommunication setups. For utilities looking to upgrade their communication capabilities while maintaining existing power lines—think smart grids—OPGW shines as an ideal solution due to its dual functionality in both data transmission and grounding protection.
On the flip side, if your project involves installing a new telecommunications network where there are no existing power lines or you need flexibility regarding pole placements—ADSS takes center stage here with its self-supporting design that adapts easily to various environments without compromising signal quality or reliability. Ultimately, choosing between these two formidable options boils down to understanding your project's unique demands: whether you need the integrated benefits offered by OPGW or the versatility provided by ADSS.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of OPGW cable, it’s clear that this innovative technology offers a wealth of benefits for modern infrastructure. From its dual role in power transmission and communication to its robust design that withstands environmental challenges, OPGW stands out as a vital component in today’s energy grids. Understanding the nuances of OPGW, including concepts like OPGW splicing and the differences between OPGW and Earth Wire or OPPC, helps stakeholders make informed decisions that enhance system reliability.
Recap of OPGW Cable Benefits
OPGW cable is not just an ordinary component; it plays a crucial role in the efficiency of electrical grids. Its ability to combine optical fiber communication with overhead power lines makes it unique, allowing for real-time monitoring and enhanced data transmission capabilities within the grid. Additionally, understanding what is the difference between OPGW and ADSS fiber optic cable can help organizations select the best solution based on their specific needs.
Future Trends in OPGW Technology
Looking ahead, we can expect exciting advancements in OPGW technology that will further improve its performance and adaptability. Innovations may include enhanced materials for greater durability against extreme weather conditions and smarter integration with IoT devices for better monitoring capabilities across transmission lines. As we explore what is the difference between OPGW and OPPC, it's evident that these developments will position OPGW as a leading choice for future-proofing infrastructure.
Why Spark Fittings is a Trustworthy Partner
When it comes to sourcing high-quality OPGW solutions, Spark Fittings emerges as a reliable partner you can trust. Their expertise not only covers the technical aspects of products like OPGW splicing but also extends to offering tailored solutions that meet your specific requirements. With Spark Fittings by your side, you're not just investing in products; you're building a partnership aimed at enhancing your infrastructure's resilience through effective use of technologies such as OPGW in transmission lines.

