Introduction

Overhead transmission lines are the veins of our electrical infrastructure, transporting power from generation sources to homes and businesses. Understanding the composition of power lines is crucial for grasping how electricity flows efficiently and safely. This exploration into overhead power line components not only highlights their significance but also sheds light on the intricate systems that keep our lights on.
Understanding Overhead Transmission Lines
What is the composition of a power line? At its core, an overhead transmission line consists of various components that work together harmoniously to ensure reliable electricity delivery. These structures include conductors, insulators, and supporting elements like towers and poles, each playing a pivotal role in maintaining system integrity.
The Importance of Power Line Components
The components of a power transmission system are not merely functional; they are essential for safety and efficiency. High-quality overhead line components reduce energy loss during transmission while protecting against environmental factors such as wind, ice, and lightning strikes. Understanding these parts allows us to appreciate the engineering marvels that enable modern society to thrive.
Overview of Power Transmission Systems
Power transmission systems encompass everything from generation facilities to distribution networks, with overhead lines serving as vital links in this chain. These systems rely heavily on robust structures to withstand various stresses while ensuring optimal performance over long distances. By delving into what are the structures of power lines, we can better understand how they contribute to a stable energy supply for communities worldwide.
Core Components of Overhead Power Lines
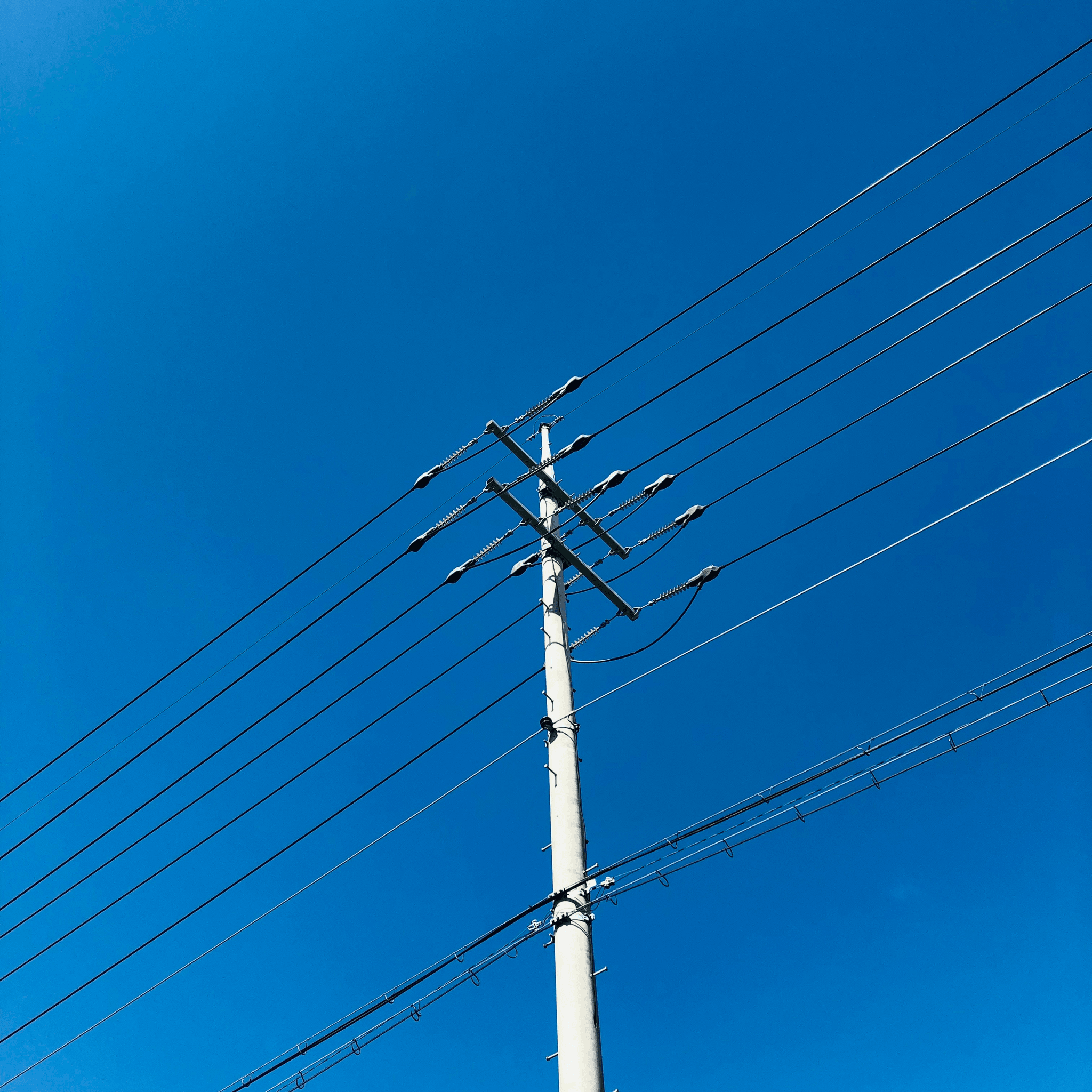

Understanding the core components of overhead power lines is essential to grasping how electricity travels from generation points to our homes and businesses. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transmission and maintaining the reliability of the system. In this section, we will delve into the key components that make up an overhead power line, including conductors, insulators, and supporting structures.
Conductors: The Heart of Transmission
Conductors are often referred to as the heart of transmission within overhead power line components because they carry electrical current over long distances. Typically made from materials such as aluminum or copper, these conductors must be carefully selected based on their conductivity, weight, and cost-efficiency. The composition of power line conductors directly affects overall efficiency; for instance, aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective than copper, making it a popular choice for many utility companies.
In addition to traditional conductors, aerial bundled cables (ABCs) have gained popularity due to their enhanced safety features and reduced risk of electrical faults. These bundled configurations minimize electromagnetic interference and are less prone to damage from wind or falling branches. Ultimately, selecting the right conductor type not only impacts performance but also influences maintenance costs and longevity in an overhead transmission system.
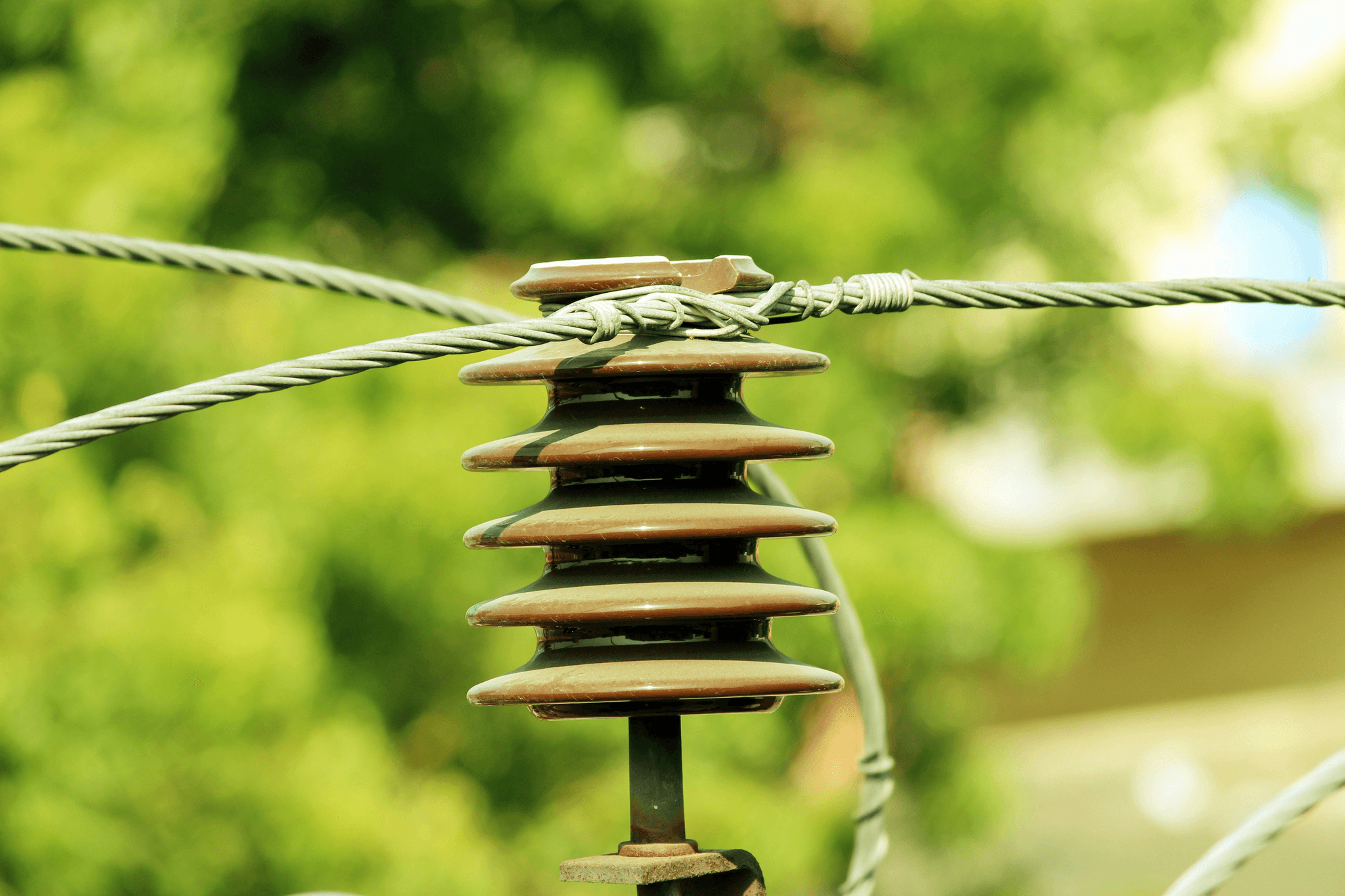
Insulators: Keeping the Current in Check
Insulators serve a critical function in any overhead power line by preventing unwanted energy loss and ensuring that electrical currents remain confined within their designated paths. Made from materials like glass or porcelain, these insulators maintain a safe distance between conductive elements and supporting structures while withstanding environmental stressors such as wind or rain. When exploring what is the composition of powerline insulators, one finds that modern composite materials have also emerged as strong contenders due to their lightweight properties and resistance to degradation.
The choice between glass vs. porcelain insulators often depends on factors such as climate conditions and installation preferences; each has its own advantages regarding durability and performance under various circumstances. Composite insulators represent a modern solution that combines lightweight design with high mechanical strength—ideal for areas prone to severe weather conditions or pollution-related challenges. Understanding how these insulator types function helps answer questions about what are the components of a power transmission system.
Towers and Poles: The Backbone of Support
Towers and poles form the backbone of support for overhead lines by holding conductors aloft while ensuring safety standards are met throughout transmission networks. Lattice towers offer robust stability with their triangular designs but require more space than monopoles which provide a sleeker profile ideal for urban settings where space is limited. When considering what are the structures of power lines, it’s clear that each design has its unique applications based on terrain type, required height clearance, and environmental factors.
The materials used in constructing these supporting structures can range from steel to concrete depending on local regulations or specific engineering needs; steel towers are particularly favored for their strength-to-weight ratio while concrete poles offer durability against weather-related wear-and-tear over time. Additionally, structure height plays an essential role in determining how effectively electricity can be transmitted over varying distances while minimizing interference with other infrastructure like buildings or trees nearby—factors vital for maintaining reliable service across regions.
Conductors: Types and Materials
Aluminum vs. Copper Conductors
Aluminum and copper are two primary materials used in overhead power line components, each with its unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Aluminum conductors are lighter and more cost-effective than copper, making them popular for long-distance transmission where weight is a critical factor. However, copper's superior conductivity means that it can carry more current over shorter distances without overheating, which raises questions about what is the composition of power line materials best suited for specific applications.
In terms of durability and resistance to corrosion, aluminum might have an edge due to its natural oxide layer that protects against wear over time. Nevertheless, copper's longevity often makes it a preferred choice in urban settings where space is limited and reliability is paramount. Ultimately, understanding what are the components of a power transmission system helps engineers select the right conductor based on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Aerial Bundled Cables and Their Benefits
Aerial bundled cables (ABCs) represent an innovative solution in modern overhead power line construction that combines multiple conductors into a single insulated bundle. This design minimizes electrical interference while enhancing safety by reducing exposure to accidental contact or environmental hazards—a significant advantage when considering what are the structures of power lines today. Furthermore, ABCs have lower wind-induced vibrations compared to traditional bare conductors.
One major benefit of using aerial bundled cables lies in their ability to reduce installation costs; fewer poles may be needed due to their compact nature while also providing improved aesthetics in residential areas—no more unsightly wires crisscrossing neighborhoods! Additionally, ABCs help mitigate issues related to tree interference since they can be installed closer together without compromising safety or functionality. With these advantages in mind, it's clear that aerial bundled cables play an essential role in enhancing overhead power line components.
Selecting the Right Conductor for Efficiency
Choosing the right conductor is crucial for maximizing efficiency within any overhead transmission system; after all, not all situations call for aluminum or copper alone! Factors such as load requirements, distance between substations, environmental conditions (like temperature fluctuations), and even local regulations must be taken into account when determining what is the composition of powerline systems best suited for specific projects.
Engineers often rely on detailed calculations regarding resistance loss versus current capacity before making decisions about conductor types—ensuring optimal performance while minimizing energy waste throughout distribution networks across cities or rural areas alike! Additionally, advancements in technology have led to innovative materials being introduced into this field—such as high-temperature superconductors—that promise even greater efficiency gains down the road.
Ultimately understanding how different conductor options impact overall performance empowers stakeholders involved with designing effective solutions tailored specifically towards unique challenges faced during installation processes associated with various types' overhead line component configurations available today!
Insulators: Function and Types
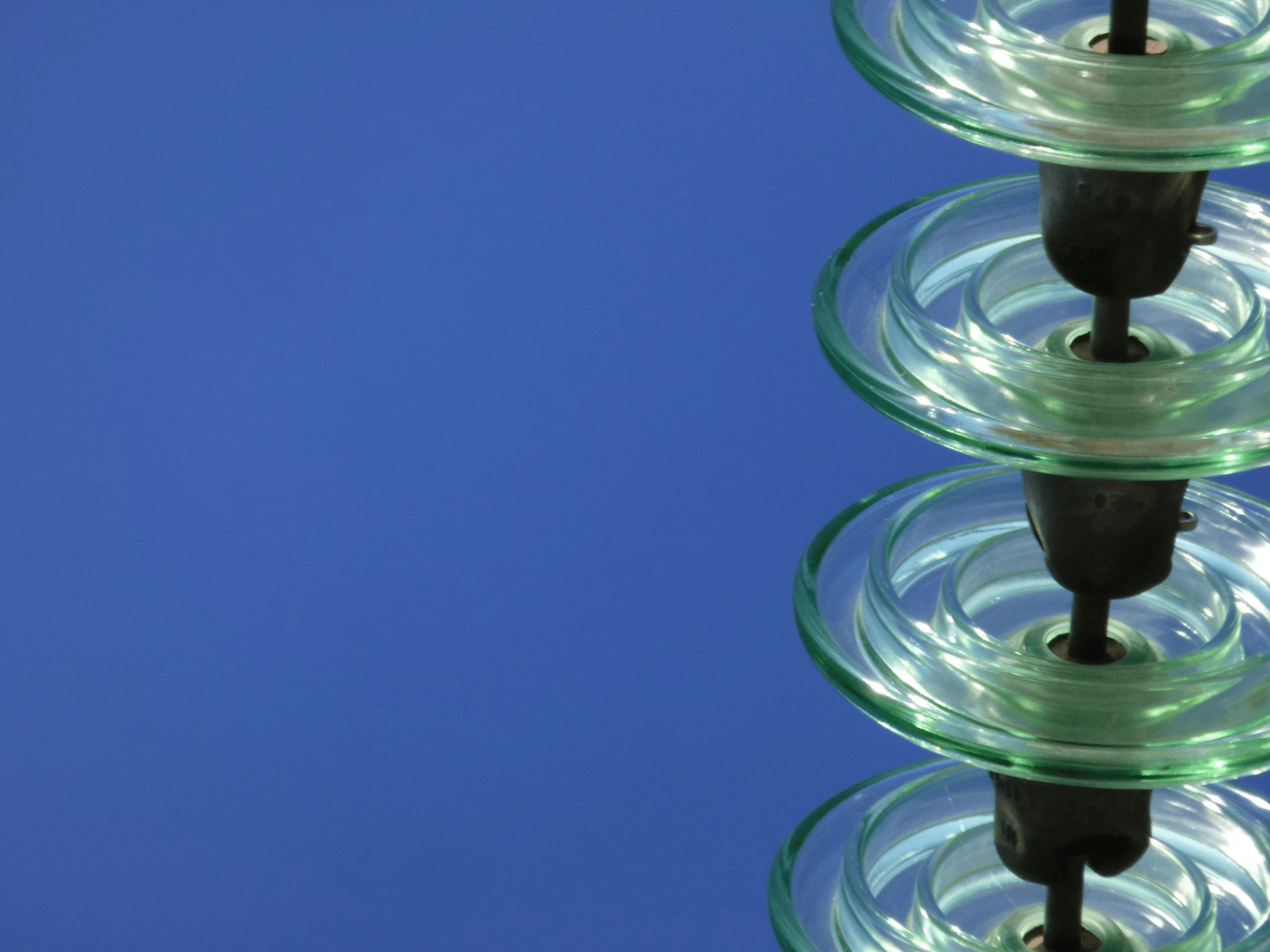

Insulators play a crucial role in the functionality of overhead power lines, ensuring that electricity flows without interruption while keeping the current safely contained. These vital power line components prevent electrical leakage to surrounding structures, maintaining efficiency and safety in power transmission systems. Understanding the different types of insulators and their applications is essential for anyone curious about what is the composition of power lines.
Glass vs. Porcelain Insulators
When discussing insulator materials, glass and porcelain are often compared due to their unique properties and historical significance in overhead power line components. Glass insulators are known for their high dielectric strength and resistance to weathering, making them a reliable choice for various environmental conditions. On the other hand, porcelain insulators offer excellent mechanical strength and can withstand extreme temperatures, making them a staple in many power transmission systems.
Both materials have distinct advantages; glass insulators tend to be more transparent to radio frequencies, which is beneficial for communication lines that share space with power lines. However, porcelain's durability makes it a preferred option in areas prone to vandalism or severe weather conditions. Ultimately, choosing between these two types often depends on specific project requirements and local environmental factors.
Composite Insulators: The Modern Solution
In recent years, composite insulators have emerged as a modern solution within overhead line components that offer several benefits over traditional materials like glass or porcelain. Made from polymer materials combined with fiberglass rods, these insulators are lightweight yet incredibly strong, making installation easier and reducing transportation costs significantly. Their design also provides enhanced resistance against pollution and moisture accumulation—common culprits behind electrical failures.
Composite insulators can outperform traditional options in terms of longevity because they resist cracking or breaking when exposed to harsh environmental conditions. As utility companies seek innovative ways to improve reliability while minimizing maintenance costs, composite insulators represent an exciting advancement in what are the components of a power transmission system today. They combine modern technology with practical application to meet contemporary demands effectively.
Key Factors Affecting Insulator Performance
Several key factors affect the performance of insulators used in overhead power lines, influencing their effectiveness as critical components within electrical infrastructure. Environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and pollution levels can significantly impact how well an insulator functions over time—these elements must be considered when determining what are the structures of power lines best suited for specific regions.
Additionally, mechanical stress from wind loads or ice accumulation can strain both glass and porcelain types; hence proper selection based on location is vital for ensuring long-term reliability. Regular inspections also play an essential role since wear-and-tear can lead to reduced performance levels if not addressed promptly—this highlights why understanding each type's strengths is crucial when evaluating overall system integrity.
In summary, whether utilizing classic glass or porcelain options or embracing modern composite solutions within overhead transmission systems' design framework requires careful consideration of multiple factors affecting performance outcomes across diverse environments.
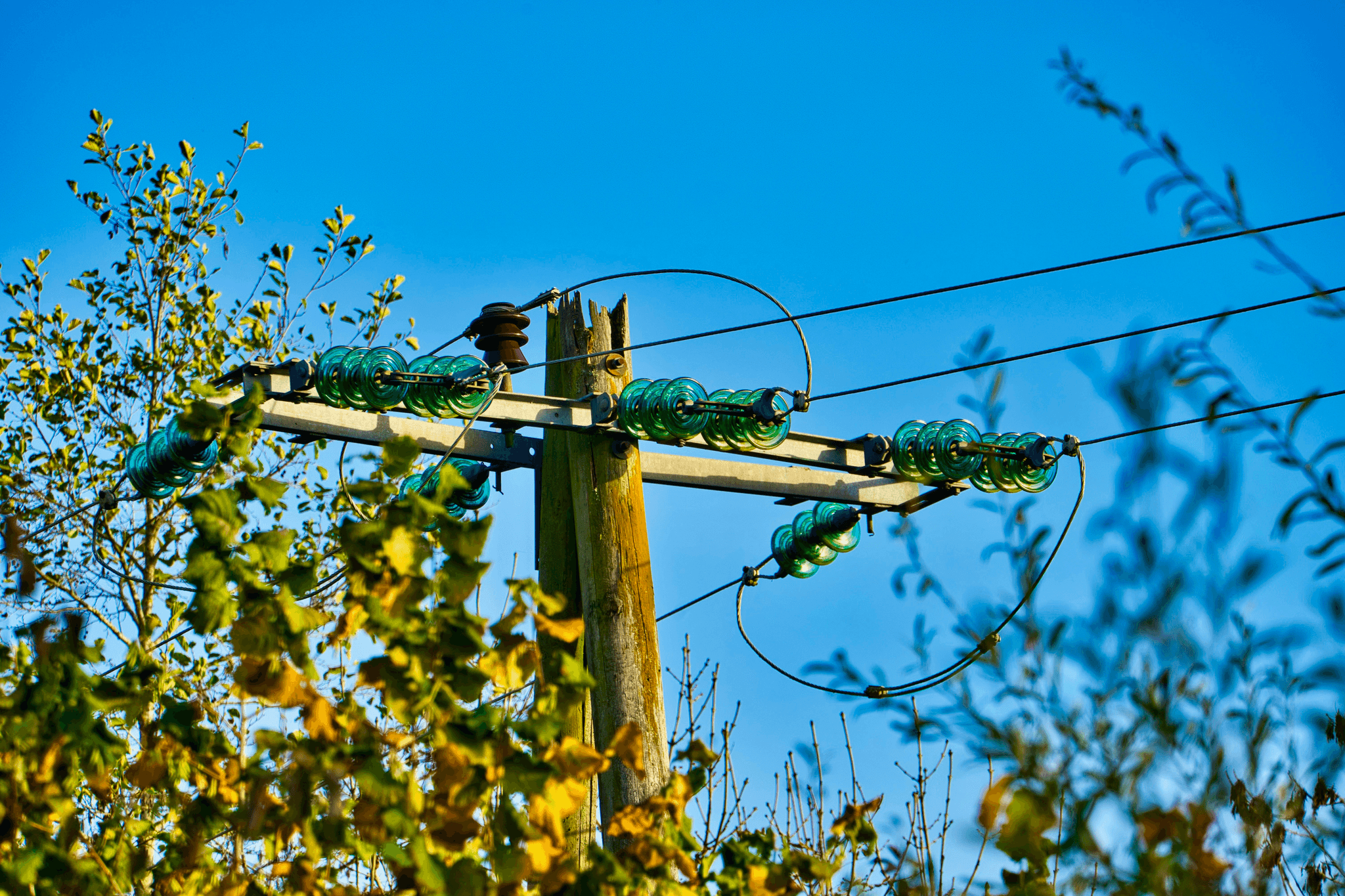
Supporting Structures: Towers and Poles
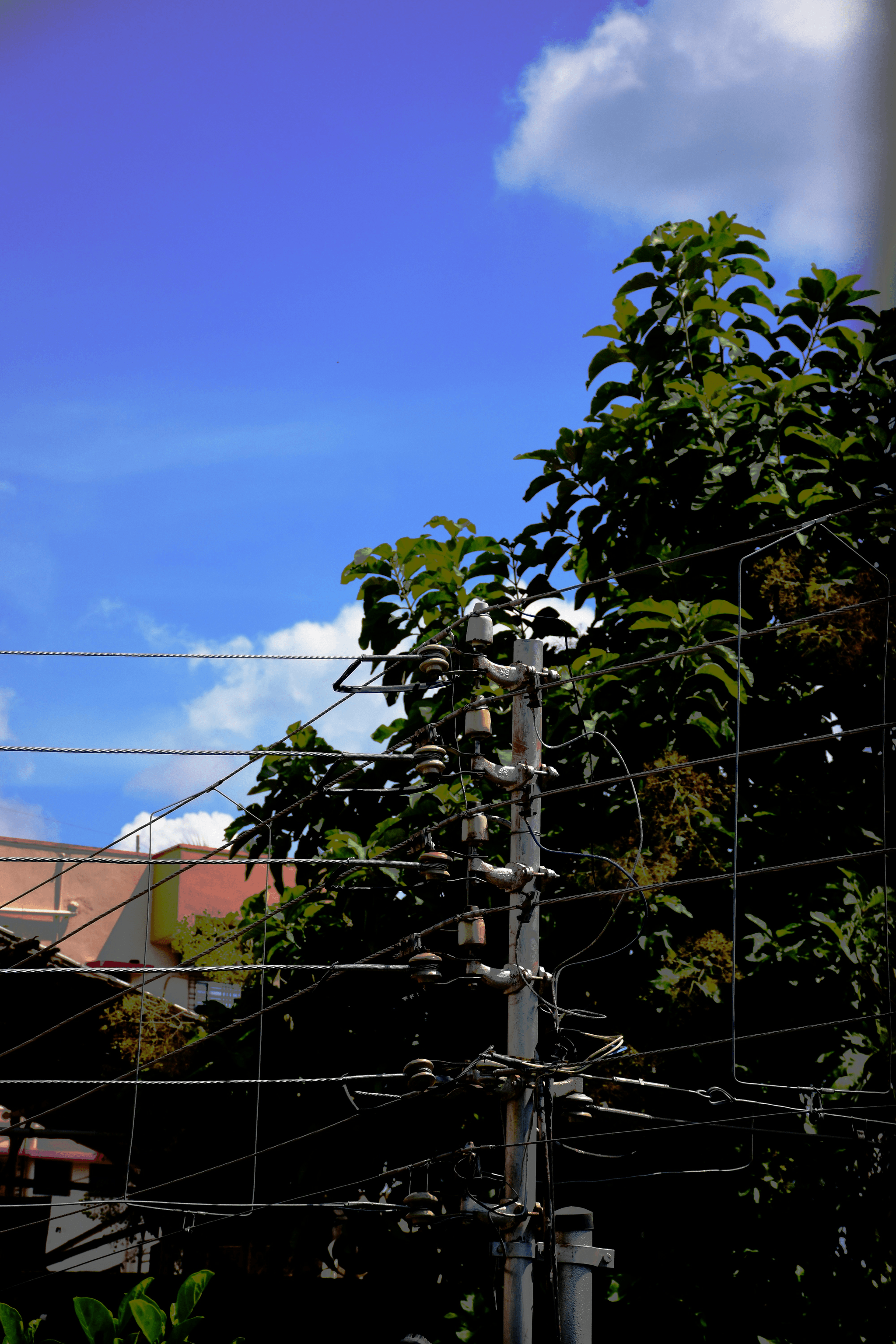

When it comes to overhead power lines, the supporting structures—namely towers and poles—play a crucial role in ensuring stability and safety. These structures are designed to withstand various environmental factors while maintaining the integrity of power line components. Understanding what these structures are made of and how they function can illuminate the complexities of power transmission systems.
Lattice Towers vs. Monopoles
Lattice towers and monopoles are two primary types of supporting structures for overhead power lines. Lattice towers, characterized by their triangular framework, offer strength and stability while using less material than solid poles, making them a cost-effective choice for high-voltage applications. On the other hand, monopoles provide a sleek, modern aesthetic with their single-pole design but may require more robust materials to achieve similar load-bearing capabilities as lattice towers.
The choice between these two types often boils down to specific project requirements such as location, environmental impact, and budget considerations. For instance, lattice towers can be advantageous in areas where wind loads are a significant concern due to their ability to distribute stress effectively across multiple points. Conversely, monopoles may be favored in urban settings where space is limited or aesthetic considerations are paramount.
Ultimately, understanding the differences between lattice towers and monopoles helps answer the question: what are the structures of power lines? Each type has its unique advantages that contribute to the overall efficiency of an overhead transmission system.
Materials Used in Supporting Structure Construction
The materials used in constructing supporting structures for overhead power lines significantly influence their durability and performance. Common materials include steel for lattice towers due to its high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion when properly treated; aluminum is another option due to its lightweight properties but is less commonly used for main support structures. Monopoles often utilize galvanized steel or reinforced concrete for added resilience against environmental factors like wind or ice accumulation.
Choosing the right materials is crucial not only for structural integrity but also for minimizing maintenance costs over time—a vital consideration in any discussion about what is the composition of power line infrastructure? The longevity of these components directly impacts overall efficiency within power transmission systems by reducing downtime caused by repairs or replacements.
In addition, advancements in material science have led to innovations such as composite materials that combine lightweight properties with enhanced strength characteristics—further optimizing what we know about overhead line components today.
Impact of Structure Height on Transmission
The height of towers and poles plays an essential role in determining how effectively an overhead power line transmits electricity across distances. Taller structures can facilitate greater clearance from ground level obstacles such as trees or buildings while also minimizing electromagnetic interference with nearby environments—a common concern among communities near high-voltage lines.
Moreover, increased height allows for longer spans between supports; this reduces the number of required structures along a route which can save both time during installation and costs associated with construction—addressing questions like what are the components of a power transmission system? However, taller structures must be engineered carefully to withstand wind loads at elevation without compromising stability.
Ultimately, understanding how structure height impacts transmission efficiency provides valuable insight into planning effective overhead power line networks that meet growing energy demands while ensuring safety standards remain uncompromised.
Spark Fittings: Optimizing Power Line Components

When it comes to overhead power lines and components, the importance of quality accessories cannot be overstated. Spark Fittings specializes in providing essential products that enhance the performance and reliability of power transmission systems. In this section, we will explore the various offerings from Spark Fittings and how they contribute to the overall efficiency of overhead line components.
Introduction to Spark Fittings’ Products
Spark Fittings offers a comprehensive range of products designed specifically for overhead power lines and components. Their lineup includes everything from armor rods to tension clamps, all crafted with precision to meet industry standards. Understanding what is the composition of power line accessories is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in any power transmission system, making Spark Fittings a go-to choice for utility companies.
The company’s commitment to innovation means that they continually adapt their product offerings based on emerging technologies and customer feedback. This dedication ensures that their products not only meet but exceed expectations in terms of durability and functionality. By integrating these high-quality components into your overhead line component setup, you can significantly enhance the reliability of your entire transmission network.
Importance of Armor Rods and Tension Clamps
Armor rods play a pivotal role in protecting conductors from abrasion and wear caused by environmental factors or mechanical stress. These essential power line components help extend the lifespan of conductors by distributing mechanical loads more evenly across their surface. When considering what are the structures of power lines, it’s clear that incorporating armor rods can greatly reduce maintenance costs over time.
Tension clamps are equally important as they secure conductors at various points along the transmission line, ensuring stability even under challenging conditions like high winds or ice accumulation. These clamps provide necessary support while allowing for some flexibility during expansion or contraction due to temperature changes—a critical factor when assessing what is the composition of powerline systems.
By investing in quality armor rods and tension clamps from Spark Fittings, utilities can optimize their infrastructure for enhanced resilience against nature's whims while maintaining efficient energy flow.
Enhancing Reliability with Quality Accessories
The overall reliability of a power transmission system hinges significantly on its individual components; hence, choosing quality accessories is paramount. Quality spark fittings ensure seamless connections between various overhead line components while minimizing energy losses due to poor conductivity or mechanical failure. This level of attention to detail answers questions about what are the components of a power transmission system by highlighting how even small parts contribute immensely to operational success.
Moreover, using top-notch accessories not only enhances performance but also promotes safety within electrical networks—an aspect often overlooked when discussing overhead line component optimization. When all elements function harmoniously together—conductors, insulators, towers—the entire system becomes more robust against external stresses and internal inefficiencies.
In summary, incorporating high-quality spark fittings into your overhead power lines can lead directly to improved operational efficiency and reduced long-term costs associated with maintenance or replacements—making them indispensable in modern energy infrastructure.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of overhead power lines and their components, it’s clear that understanding what makes up these systems is vital. The composition of power line infrastructure includes conductors, insulators, towers, and various supporting structures, each playing a pivotal role in efficient electricity transmission. By grasping the intricacies of these overhead line components, we can appreciate the engineering marvels that keep our lights on.
Recap of Overhead Power Line Composition
The composition of powerline systems is a blend of essential elements working together seamlessly. Conductors serve as the heart of transmission, while insulators ensure safety by preventing unwanted electrical discharges. Towers and poles provide the necessary support to elevate these components above ground level, showcasing how every aspect contributes to the overall functionality of overhead power lines.
The Role of Components in Power Transmission Systems
When considering what are the components of a power transmission system, it's important to recognize their interdependence. Each part—conductors for carrying current, insulators for protection against electrical faults, and towers for structural integrity—plays a unique role in ensuring reliable energy delivery. Together, these power line components create a robust network that can withstand environmental challenges while delivering electricity efficiently.
Future Innovations in Power Line Engineering
Looking ahead at future innovations in power line engineering reveals exciting advancements on the horizon. Emerging technologies aim to enhance conductor materials for better efficiency and durability while introducing smarter insulator designs that can adapt to varying conditions. As we continue to innovate within the structures of power lines, we pave the way for more sustainable and reliable energy solutions.

